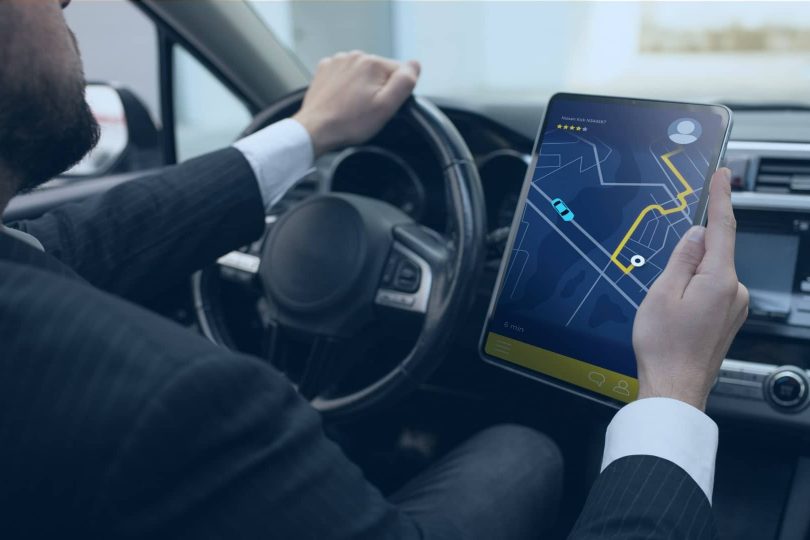
Understanding Vehicle Monitoring System
In today’s fast-paced world, the concept of a Vehicle Monitoring System (VMS) has emerged as a cornerstone in managing and maintaining vehicle fleets. A VMS is a comprehensive tool that employs advanced technology to monitor, analyze, and manage vehicles remotely. This system is not just a trend; it’s a revolution in how we interact with and manage vehicles, ensuring efficiency, safety, and optimization.
Types of Vehicle Monitoring System
Vehicle monitoring systems can be classified into several types based on their functionality:
- GPS Tracking Systems: These systems use Global Positioning System technology to provide real-time location tracking of vehicles.
- Diagnostic Monitoring Systems: They focus on monitoring the vehicle’s mechanical and engine status, sending alerts for maintenance and potential issues.
- Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems: These systems analyze driver behavior, including speed, braking patterns, and adherence to traffic rules.
- Fuel Monitoring Systems: They track fuel usage, helping in optimizing fuel consumption and reducing expenses.
How Do Vehicle Monitoring Systems Work?
A vehicle monitoring system integrates hardware and software components. The hardware, usually a GPS device, is installed in the vehicle. It collects various data points like location, speed, engine status, and more. This data is transmitted via cellular or satellite networks to a central server. The software part of the system then analyzes this data, providing insights through a user interface. Users can access this information on their computers or smartphones, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Benefits of Vehicle Monitoring Systems
Vehicle monitoring systems offer a plethora of advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: By monitoring vehicle speed and driver behavior, VMS helps in reducing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Efficiency: Real-time tracking ensures optimal route planning, saving time and resources.
- Cost Reduction: Effective monitoring of fuel and maintenance needs leads to significant cost savings.
- Theft Prevention: Real-time location tracking can aid in quick recovery in case of theft.
- Compliance Management: Ensures that vehicles comply with regulatory requirements, avoiding penalties.
Real-World Applications of Vehicle Monitoring Systems
- Fleet Management: Businesses use VMS to manage their fleets, ensuring timely deliveries and efficient operations.
- Public Transport Systems: Monitoring buses and trains helps in maintaining schedules and ensuring passenger safety.
- Emergency Services: For ambulances and fire trucks, VMS ensures the quickest response time in emergencies.
- Personal Vehicle Monitoring: Individuals use VMS for the security and maintenance of their vehicles.
Challenges and Considerations
While VMS offers numerous benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- Privacy Concerns: Monitoring systems raise concerns about the privacy of drivers. It’s crucial to balance monitoring with respecting individual privacy rights.
- Cost of Implementation: The initial setup cost for a VMS can be high, especially for small businesses.
- Data Overload: Managing and analyzing large volumes of data can be overwhelming without proper tools.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on these systems can be problematic in case of technical failures.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the VMS is a transformative tool for modern transportation. Its ability to enhance safety, efficiency, and compliance makes it an indispensable asset for both commercial and personal use. While embracing this technology, it’s important to address the challenges and considerations to fully leverage its benefits.