Most of our trip revolves around GPS. The majority of people around the globe know what’s GPS and its use.
A short definition to have a glance can be “GPS or Global positioning satellite navigation system used to know the position of an object which is owned by US government and operated by United States Air Force.”
Other known navigation systems of the world are GLONASS of Russia, BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) of China, and Galileo of the European Union will are scheduled to be fully operational by 2020. India is a progressive country and under the “Made in India” campaign made our own navigation system “NavIC”. Let’s understand in detail if our NavIC will be useful for the world or not.
NavIC
NavIC is the operational name of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS). It stands for Navigation with Indian Constellation which is derived from the word navik which also means sailor or navigator in Sanskrit and many other Indian languages.
It is a satellite navigation system that provides real-time position with time. This system extends from India to 1,500 km around it and will extend to more areas in the future. NavIC has been in orbit since 2018 and was about to start its service in the same year. But due to the failure of a satellite new date will be soon decided.
It will be providing two types of operational services:
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS): This service will be open to all public users.
- Restricted Service (RS): This service is encrypted for authorized users including the military.
Why did NavIC come into existence?
In the 1999 Kargil War against Pakistan, the Indian military sought GPS data from nearby regions. The US government’s navigation system could have provided the information, but they denied it. The significance of having India’s own navigation system became apparent during the Kargil War.
And then, ISRO in less than 2 years brought the country closer to the goal with IRNSS.
Which are its segments?
IRNSS is divided into 3 segments:
Space Segment: This segment consists of a constellation with 7 satellites. From which 3 are GEO(Geostationary, earth, orbit or geosynchronous) and 4 GSO(Geosynchronous orbit). GEO is used for telecommunication and GSO is a communication satellite used for keeping satellite in view of its station and receivers.
Ground Segment: This segment is useful for the operation and maintenance purposes of the IRSS constellation. They are;
- IRNSS Spacecraft Control Facility (IRSCF)
- ISRO Navigation Centre (INC)
- IRNSS Range and Integrity Monitoring Stations (IRIMS)
- IRNSS Network Timing Centre (IRNWT)
- IRNSS CDMA Ranging Stations (IRCDR)
- Laser Ranging Stations
- IRNSS Data Communication Network(IRDCN)
User Segment: They design it with the receiver and antennas to capture the IRNSS signals. The user segment comprises two types of receivers which are:
- Single-frequency IRNSS receiver that receives SPS/RS signal at L5 or S-band frequency. It is capable of doing corrections in the ionosphere.
- Dual-frequency IRNSS receiver which receives SPS/RS signal in both L5 and S-band frequencies can track more than one radio signal from different satellites with various signals.
What are the applications of NavIC?
- Land, Sky, and Water Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle GPS tracking and efficient fleet management
- Integration with Smartphones and other handheld devices
- Precise timing
- Mapping and accurate GPS data capturing
- Real-time Visual and Audio navigation for drivers
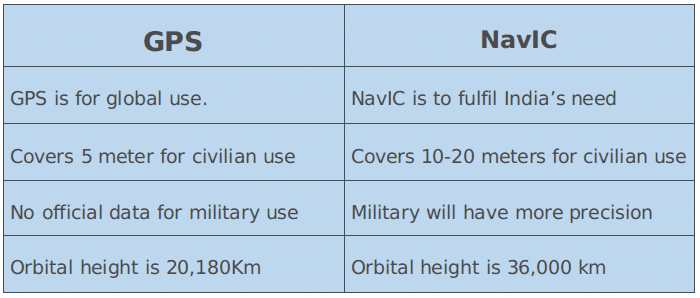
What are the difference between NavIC and America’s GPS?
Conclusion
NavIC is India’s and ISRO’s opportunity to prove to the world its power and dignity. It will also provide faster and more efficient navigation data. The important thing is soon we will be using our own navigation system. Happy Tracking.





